

Bi-axial stretching of PLA and improvment of water barrier properties.
We also studied the mechanical behavior and associated structural evolution of PLA upon bi-axial stretching. Besides, we finely characterize strain-induced structure in terms of both nature of phase and orientations.
We also carried out a study on the water barrier properties of bi-axially stretched PLA (In collaboration with the LECAP team). Interestingly, we observed that while thermally induced crystallinity has no effect on the water barrier properties, bi-axial stretching signifcantly improve the impermeability of PLA.
Evidence of the formation of a mesomorphic phase :
In-situ following of strain-induced structural evolution upon uni-axial stretching by means of WAXS and SAXS reveals that the strain-induced structure was strongly sensitive to the stretching conditions. Besides WAXS experiments show that, for some drawing conditions, some kind of paracrystalline structure is induced into PLA upon uniaxial stretching. Such kind of phase, encountered in the case of PET, is a mesomorphic phase. It is desbribed by aligned parallel macromolecular chains without correlations in the two other directions.
This mesomorphic phase can be evidenced by means of WAXS and FTIR with a characteristic band around 918 cm-1.
During my PhD, I develop deconvolution methods in order to describe the mesomorphic phase but also in order to quantify it. Up to now, this mesophase has only been obtained from mechanical treatments but i believe that it's possible to obtain it by thermal ones. Regarding this topic, we also shown that the mesomorphic phase rather correspond to some kind of frustrated state, and that it is not a transient state between amorphous and crystal, or in other words that the mesomorphic phase do not act as a precursor for crystallization.
Some things I've done

Relationships between the nature of the strain-induced ordered phase and molecular mobility
In order to understand the origin of the formation of this mesophase, we made a wide variety of experiments and we found that the nature of the phase induced was highly sensitive to the deformation parameters (stretching speed and temperature) used. A main result we get about this was that a crystalline phase can be induced upon stretching only if all the molecular mobilities are activated into the materials. In other words, the formation of a mesomorphic phase arises from a lack of molecular mobilities.
Influence of the D-isomer content on the strain-induced structural evolution
Something often not fully took into account when speaking of PLA is that, as this polymer is synthesized from a chiral dimer, there are different kinds of PLA. Indeed there are the two "pure polymers" PLLA and PDLA respectively but there are also a wide variety of PDLLA, ie Polylactides mainly composed of L-PLA monomers but having nevertheless D-PLA monomers. These kinds of PLA are genereally the ones that are indsutrially available, and the D-PLA content vary from 1 to 6-8%.
Previous studies have shown that the D-isomer present into the chains act as defects and slow down the crystallization kinetics. A D-isomer content above 8% even inhibit PLA crystallization and leads to a fully non crystallizable material.
Thus we studied what was the effect of the D-isomer content on the mechanical behavior and strain-induced structural evolutin. Briefly we shown that only the materials able to thermally crystallized present a strain-induced crystallization process upon stretching. Also a mesomorphic phase can be induced upon stretching when they are stretched near from their glass transition temperature for all the materials able to crystallize
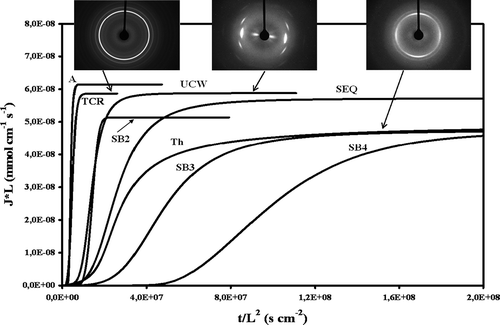
Study of the strain-induced structural evolution of Polylactides
This topic was my thesis one, thus i would have lots of things to tell you about it. Here i will just summarize you the key results we obtained. To start, Polylactide (PLA), is an aliphatic polyester synthesized from renewable resources such as corn or starch. This polymer known an increasing interest since about 10 years because it is one of the most promising "bio-polymer". Indeed in addition to be issued from bio-based, PLA is also bio-compatible, Bioresorbable and also Bio-compostable. Moreover, it exhibits good thermomechanical properties comparable to the ones of PET or PS.
Plastic deformation mechanisms involved during cold drawing
I also deeply investigate what happens during cold-drawing of PLA, i.e. when PLA is stretched below it's Tg. This part was mainly investigated by means of SAXS and it took a long time to understand what was happening due to the complexity of the PLA behavior.
Without going into details, we recently published a paper where we shown that the PLA brittle behavior at room temperature arises from the activation of the crazing mechanism. We also propose a model to explain why PLA is ductile when stretched just above ambiant temperature. I won't go into details as it may probably bored you but feel free to contact me if you want to know more about these funny SAXS patterns
Plastic deformation mechanisms during stretching of initally semi-crystalline PLA.
Elaboration and characterization of polymer nanocomposites
I started to work on polymer nanocomposites at the end of my thesis. Since, it's still one of my topic of interest and nice results have been obtained during the few months I spend in the IMCN/BSMA team. Actually, this topic still interest me and very interesting results are being obatined through the PhD Thesis of Saadia. Here i will just give you some examples of carried out works.
Morphology and thermo-mechanical properties of Polyamide 11-Montmorillonite nanocomposites elaborated by water assisted extrusion.
Polylactide - Halloysite nanocomposites elaborated by water assisted-extrusion : structure, morphology, mechanical and fire resistance.
Influence of Montmorillonite on the strain-induced structural evolution of Polylactide.
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |





Elaboration and characterization of polymer blends
I started to work on polymer nanocomposites at the end of my thesis. Since, it's still one of my topic of interest and nice results have been obtained during the few months I spend in the IMCN/BSMA team. Actually, this topic still interest me and very interesting results are being obatined through the PhD Thesis of Saadia. Here i will just give you some examples of carried out works.